3. Angular Acceleration
Rate of change of angular velocity and its components
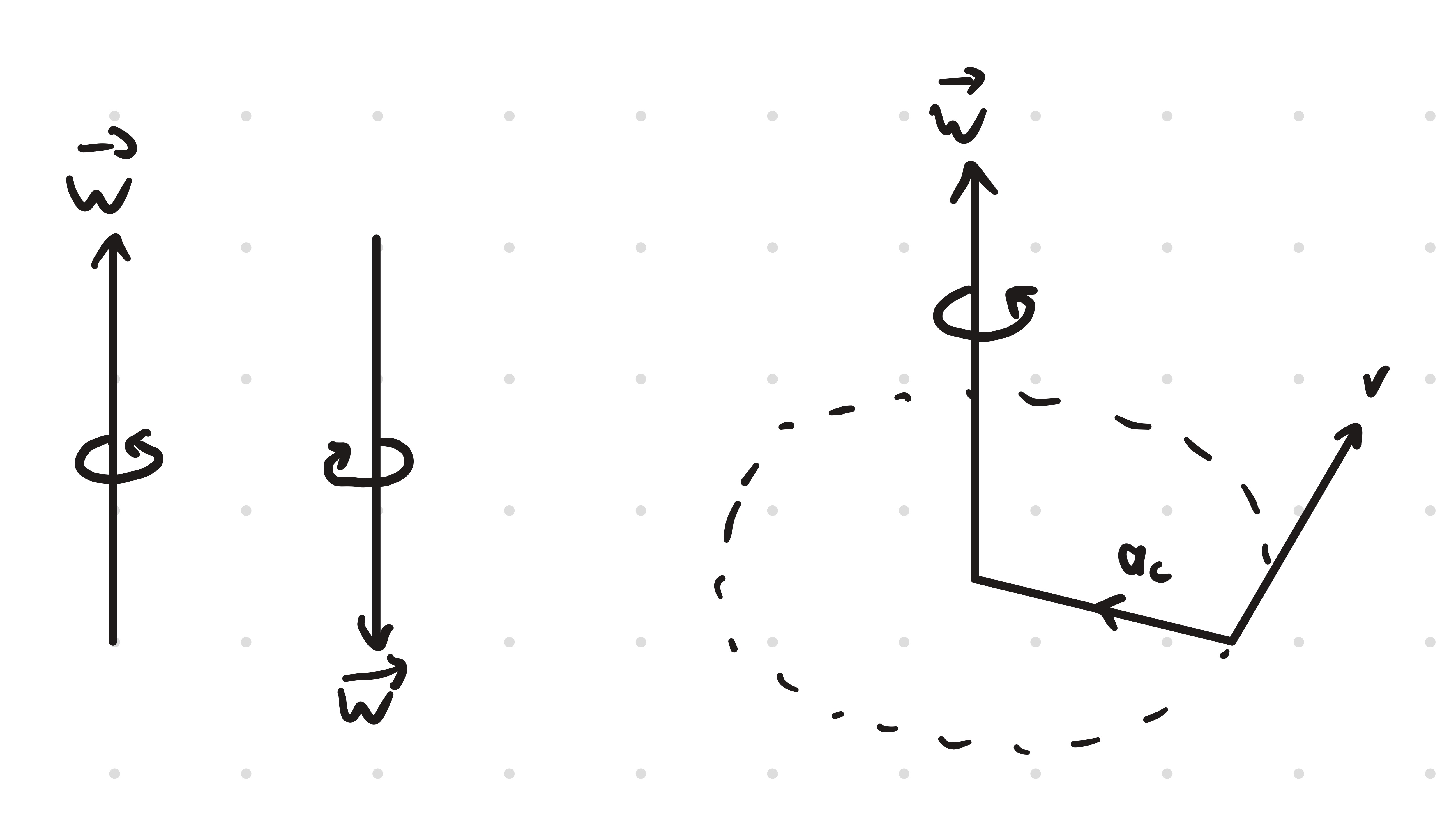
Definitions
Angular Acceleration (α)
- Rate of change of angular velocity, measured in rad/s²
Tangential Acceleration
- Changes the magnitude of the angular velocity
Radial (Centripetal) Acceleration
- Points toward the centre of the circular path and changes the direction of the velocity
Derivations
by definition, angular acceleration is
taking the limit as
for an object moving in a circle, acceleration can be decomposed into two components
deriving and , starting with
take the derivative with respect to time
this can be rewritten as
therefore, the radial (centripetal) acceleration is
and the tangential acceleration is
Constant Angular Acceleration
assuming constant angular acceleration
integrate both sides
if we solve for
Useful Equations
Example 1
A wheel starts from rest and accelerates with a constant angular acceleration of 2 rad/s². What is its angular velocity after 5 seconds?
Answer
Using with
Example 2
A disc rotates with an initial angular velocity of 4 rad/s and angular acceleration of 3 rad/s². How many radians does it rotate through in 2 seconds?
Answer
Using with