2. Circular Motion
Uniform and non-uniform motion in circular paths
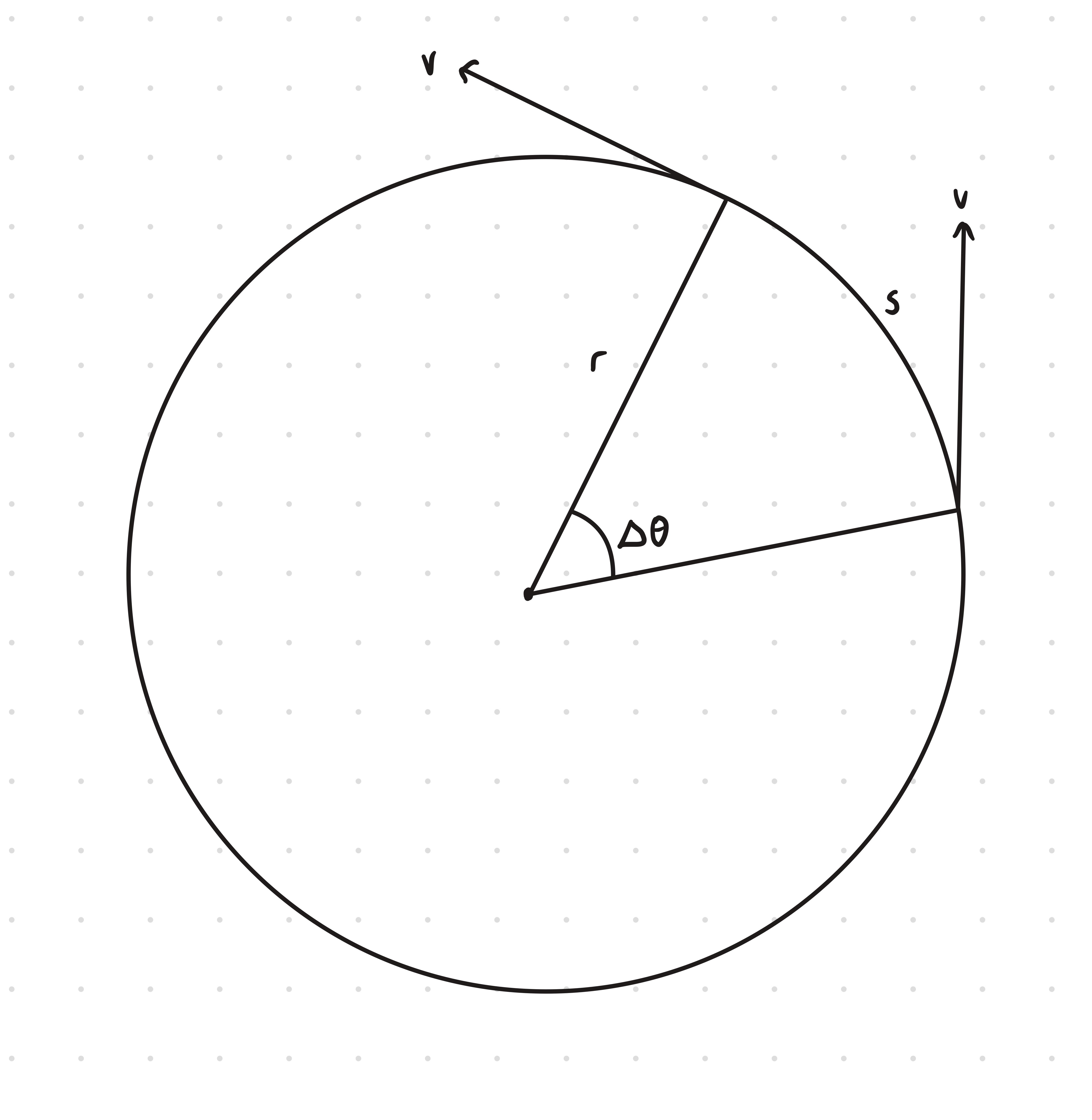
Definitions
Angular Velocity (ω)
- Rate of change of angular displacement, measured in rad/s
Centripetal Acceleration
- Acceleration directed toward the center of circular motion,
Centripetal Force
- Net force directed toward the center that keeps an object in circular motion,
Derivations
starting with arc length and linear displacement
equating these expressions
rearranging
by definition, angular velocity is the rate of change of angular displacement
taking the limit as
therefore, the relationship between linear and angular velocity is
Useful Equations
Example 1
A particle moves in a circle of radius 2 m with angular velocity 3 rad/s. What is its linear velocity?
Answer
Using
Example 2
A car travels around a circular track of radius 50 m at 20 m/s. What centripetal acceleration does it experience?
Answer
Using