4. Gravitational Potential
-----
Definitions
Gravitational Potential
- The energy an object posses due to its position in a gravitational field
- Gravitational potential energy per mass at a that point
- Work done per unit mass in bringing a mass from infinity to a defined point
- Always negative
Derivations
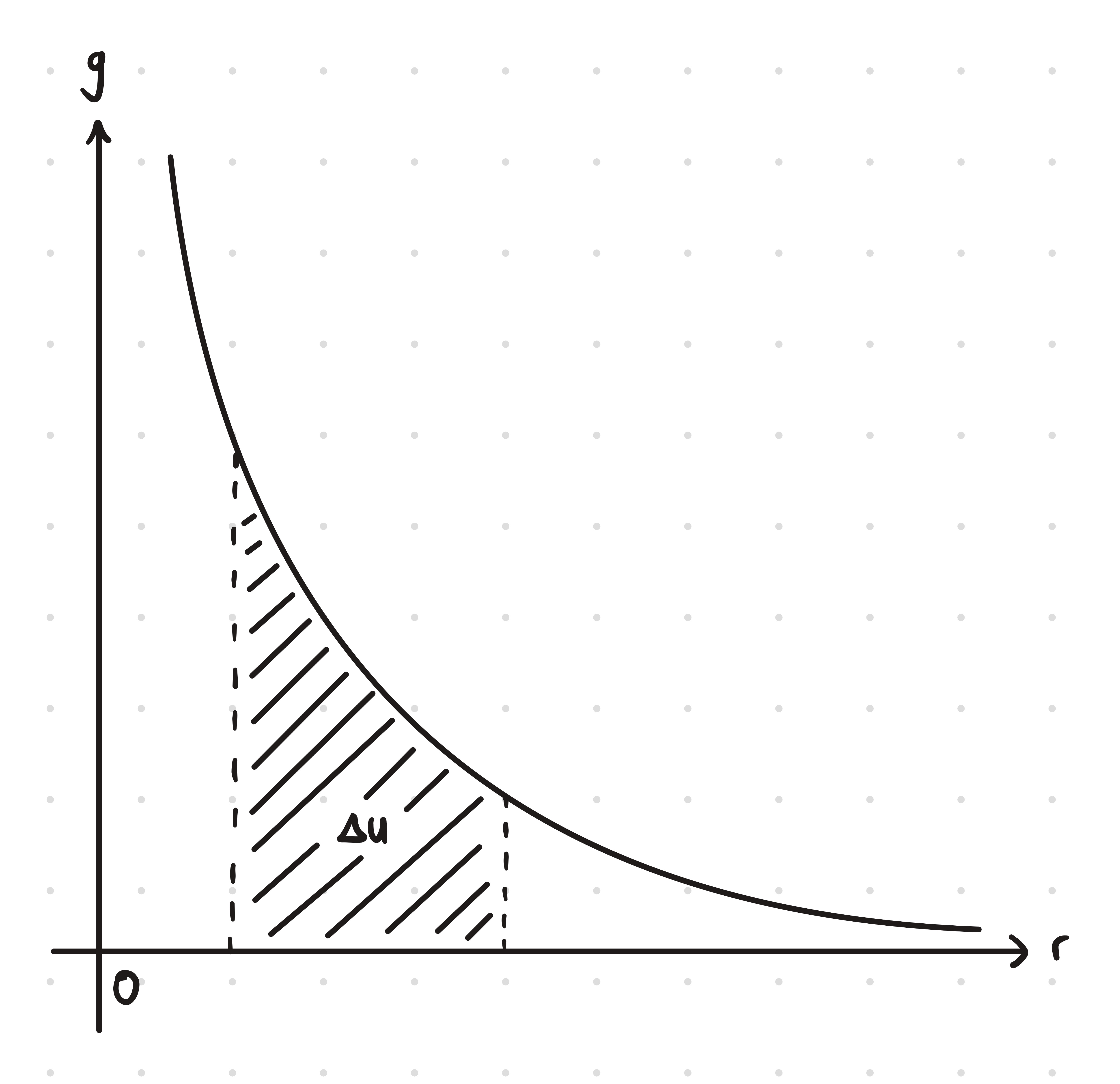
The area under the graph g-r gives you the change in gravitational potential
Work Done
Since gravitational potential equals work done per unit mass
subbing in
Integration Method
Since the change in gravitational potential is the area under the graph g-r
integrating
this results in
which looks like
which simplifies to
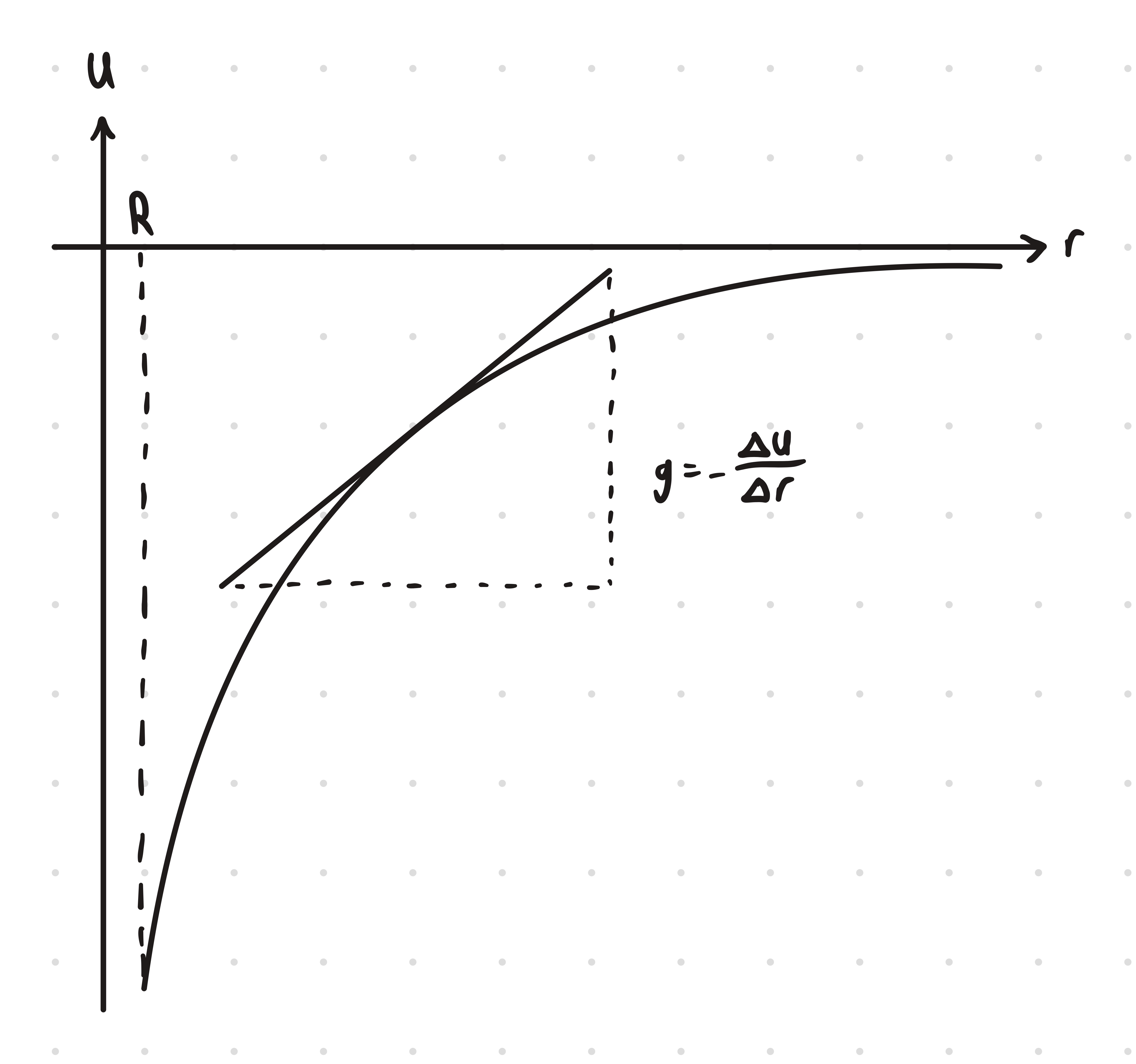
Gradient of U-r
Furthermore if you calculate the gradient of U-r you get
Useful Equations